Are you curious about healthy sperm? Do you know how to make sperm stronger for pregnancy? Looking for fresh insights on enhancing your chances of conception? You are not alone. Many individuals seek clarity on the best ways to optimize male reproductive function, whether it involves boosting sperm motility or discovering the foods that increase sperm quality. This article explores every angle of strengthening male fertility.
We will look closely at the male reproductive anatomy diagram, examine how sperm is produced, and discuss methods to identify healthy traits in those microscopic cells. We will also cover the essentials of a fertility test for men and investigate when it is time to consult experts. By the end, you will understand what influences sperm health, the steps to enhance it, and testosterone’s role in pregnancy. Read on to learn more about male reproduction explained in simple, straightforward terms.
A Brief Introduction to the Male Reproductive System
What Does the Male Reproductive System Do?
The male reproductive system creates and transports sperm cells, also known as the male gametes. These tiny cells unite with the female ovum during fertilization, forming an embryo if conditions are right. Alongside sperm production, this system is responsible for producing hormones, including testosterone. The reproductive hormones regulate libido, muscular growth, and many other bodily processes. Without healthy hormone levels, sperm development and overall fertility can decline.
The Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
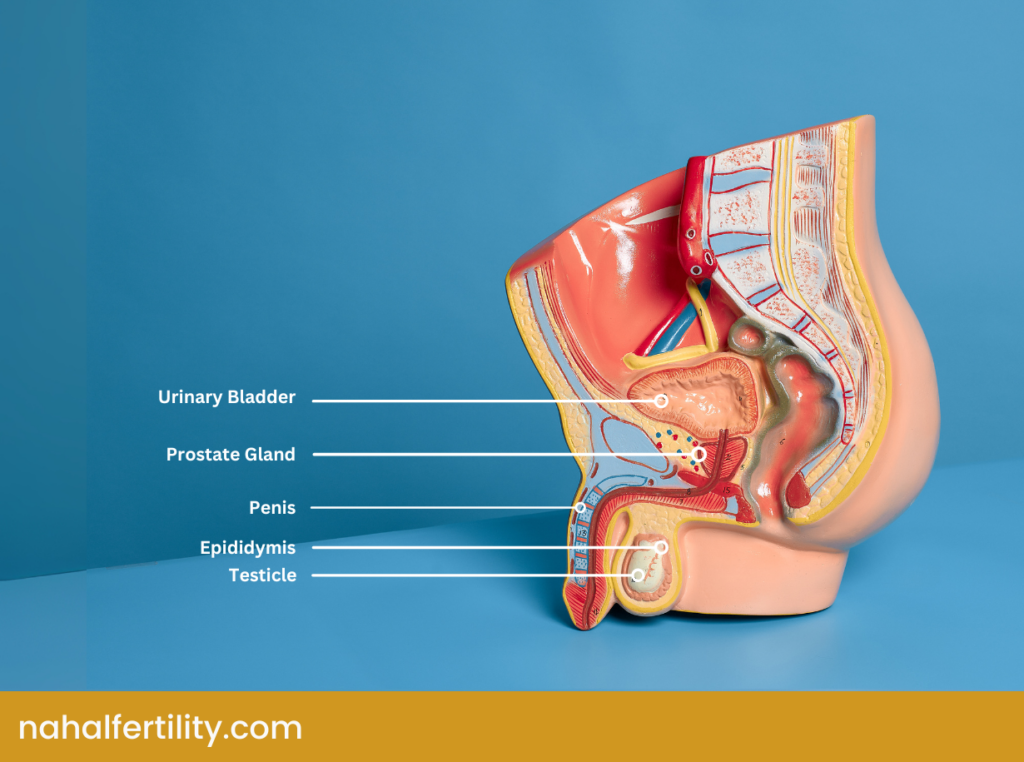
Understanding the male reproductive system’s structure is critical when trying to boost fertility. Diagrams often depict both the internal and external components necessary for sperm production and delivery. Each part plays a specific role in shaping sperm health, from providing nourishment to moving the cells toward their destination.
Internal Parts of the Male Reproductive System
- Testes (Testicles): These two glands inside the scrotum are the factories for sperm creation. They also release testosterone, which influences sperm quality and influences features like facial hair.
- Epididymis: Each epididymis stores sperm, allowing them to mature fully before they exit the body.
- Vas Deferens: Also called the ductus deferens, this tube transfers sperm from the epididymis to the urethra.
- Seminal Vesicles and Prostate Gland: These glands contribute to what is in seminal fluid by adding fructose and other substances. Their secretions help sperm survive the acidic environment inside the female reproductive tract.
External Parts of the Male Reproductive System
- Scrotum: This pouch holds the testes outside the body. Sperm production needs a slightly cooler temperature than average body heat, making the scrotum’s temperature regulation a vital factor in fertility.
- Penis: Sperm-filled semen exits the body through the urethra within the penis during ejaculation.
The Role of Sperms in Fertility
Sperm cells carry a man’s genetic information to the ovum, setting the foundation for a potential embryo. The goal is for them to travel efficiently through the female reproductive tract, penetrate an egg, and fertilize it. Every characteristic—count, morphology, motility, pH level, and more—affects the likelihood of successful fertilization. Understanding these traits is vital for anyone looking to improve fertility in man.
Sperm Production
Sperm production, or spermatogenesis, happens in the testes and is the process of making sperm cells. It starts with special cells called spermatogonia, which divide to form immature sperm cells. These cells go through a process called meiosis, which halves their genetic material to make sure they can combine with an egg. Then, they mature into sperm by growing tails for swimming, packing their DNA tightly, and getting rid of unnecessary parts. Finally, the sperm move to the epididymis, where they develop the ability to swim and fertilize an egg. This process is controlled by hormones like testosterone. The process of sperm production takes approximately 3 months.
What Determines Sperm Health?
Sperm quality rests on multiple factors, including count, motility, morphology, and specific chemical markers. A person’s age, lifestyle, environment, and hormone balance significantly impact fertility. Fertility specialists often use a sperm count test and other semen analyses to check these parameters.
1. Sperm Count or Semen Density
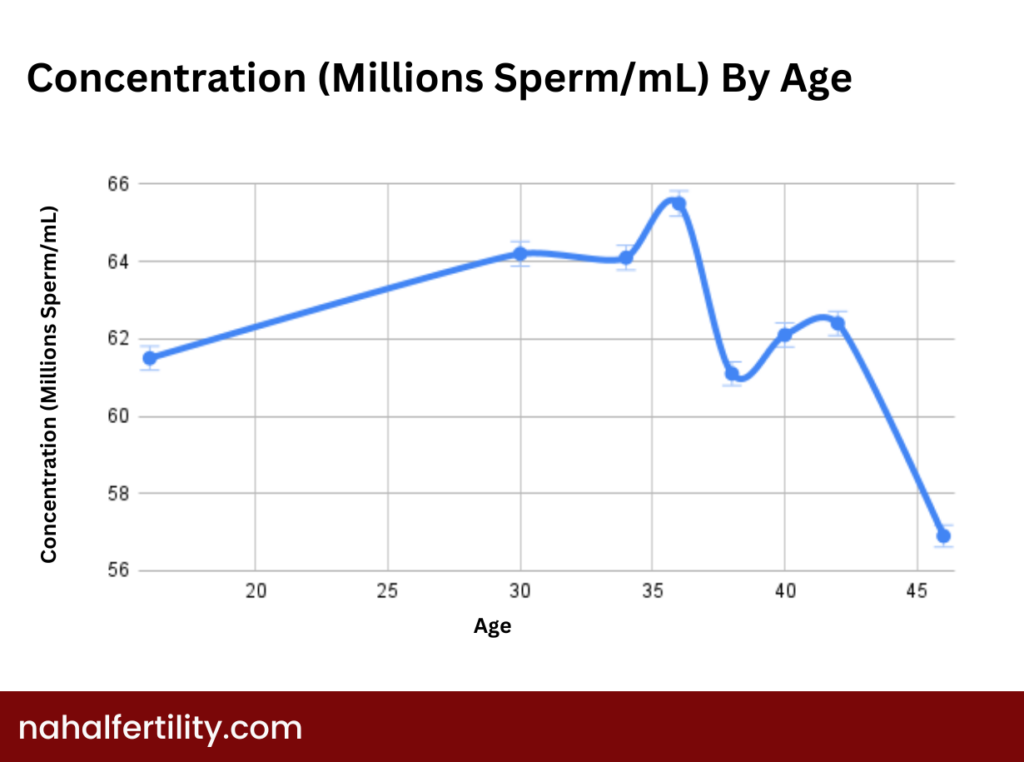
This refers to how many sperm cells appear in a specific measure of semen, typically measured in millions per milliliter. High sperm count improves the probability of success, although it is not the only criterion for fertility.
Male Sperm Count by Age Chart
Many men wonder if age affects the quantity or function of their reproductive cells. A gradual change in male sperm count by age is common—most older individuals do experience variations in quantity or quality. While age alone does not always make fatherhood impossible, aging can contribute to reduced counts and slightly lower motility.
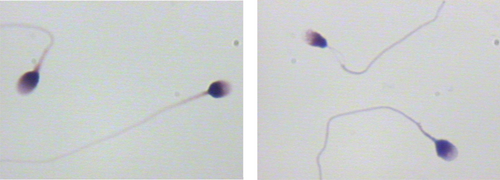
2. Sperm Movement Ability (Sperm Motility)
This trait measures how effectively sperm swim and the direction. An average sperm motility rate is key for fertilization. Poor motion means the sperm will have trouble traveling to the egg. Improving motility can sometimes involve lifestyle modifications, such as better nutrition and exercise.
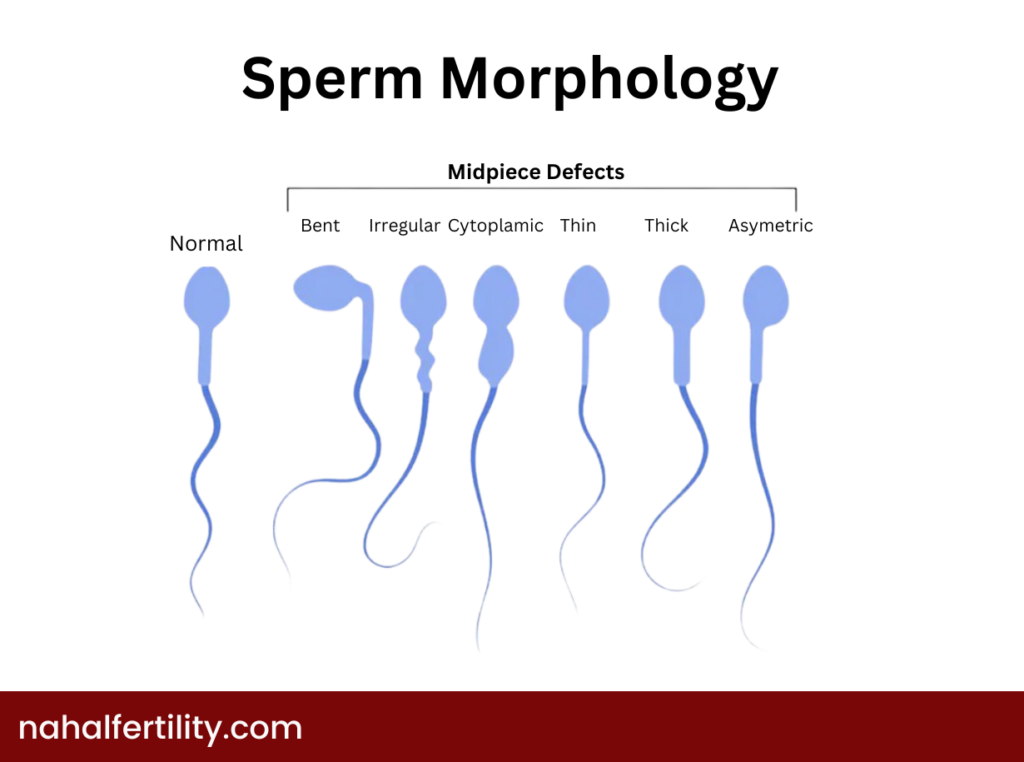
3. Sperm Structure (Sperm Morphology)
Another vital aspect is shape. Healthy sperm cells typically have an oval head and a sturdy tail. Abnormalities of sperm—like a misshapen head or multiple tails—can hinder fertilization potential. A high percentage of typical forms is beneficial.
What does a healthy sperm look like?
In the following picture, you can see the morphology of normal sperm compared to some types of defects in sperm structure.
4. Semen pH
The optimal pH ranges around neutral or slightly alkaline. Values outside normal boundaries can damage or weaken the sperm cells. Testing the acidity or alkalinity is part of a test to check male fertility and can reveal if an imbalance is harming them.
5. Semen Liquefaction Time
Semen usually liquefies within 20 to 30 minutes after ejaculation, enabling the sperm to roam freely. Delays in this process can point to issues in the fluid’s composition or the glands that produce it.
6. Testosterone Hormone Level
Reproductive health ties directly to the testosterone role in pregnancy success. Balanced levels support sperm production, sex drive, and the entire reproductive system. Low testosterone (sometimes related to stress, age, or medical conditions) may reduce a man’s ability to father a child. If you think hormone imbalance is an issue, a specialist can offer appropriate tests.
How Do You Know if Your Sperm Is Healthy?
Some men notice indirect signs of healthy sperm, such as robust sexual drive, and normal ejaculation volumes. However, the best way to check is through a professional fertility test for men, including hormonal tests and a detailed semen analysis. That evaluation detects subtle changes that might not be visible.
Signs of Healthy Sperms
- Thick, cloudy, or whitish seminal fluid: Visual clues—like a milky color—can hint at the presence of a high cell concentration. Still, color is not a perfect indicator.
- Regular Erection Quality: Consistently strong erections can sometimes correlate with balanced hormone levels.
- Adequate Ejaculate Volume: Asking, “How much ejaculate is normal?” is common. Typical volumes range around 2–5 milliliters. Each ml can contain millions of sperm cells. A sample too low in volume might indicate an underlying concern.
- Absence of Discomfort or Pain: Painless function, both before and after intercourse, is typically a good sign.
Conditions That Affect the Sperm Health
Several issues can negatively influence sperm production:
- Medical Treatments: Cancer therapies (like chemotherapy or radiation) might damage the testicles. Before starting treatments, some patients opt to freeze semen samples in a sperm bank or with their fertility clinic.
- Surgeries: A vasectomy intentionally halts sperm transport by cutting or blocking the vas deferens. Those who get it and later seek fertility will need a post-vasectomy sperm test to confirm fertility or track potential reversal outcomes.
- Infections: Certain sexually transmitted diseases or urinary tract infections can temporarily harm the cells.
- Hormone Imbalances: Thyroid or pituitary gland issues can reduce the testosterone required for sperm generation.
Lifestyle factors such as obesity, smoking, drinking alcohol, and smoking marijuana use can also exert negative effects. If you are concerned about marijuana, you might ask, “Does weed affect sperm count?” or “Does weed lower sperm count?” Research indicates that chronic heavy use can diminish fertility measures.
Symptoms of Potentially Unhealthy Sperms
- Low ejaculate volume or watery, clear fluid
- Reduced libido
- Erectile dysfunction
- Pain, swelling, or lumps in the testicular region
Consulting a fertility specialist is the best way to identify or confirm these issues. They will probably suggest tests to uncover the root cause and better understand your fertility potential
Fertility Test for Men to Analyze Sperms
A male fertility test often starts with a semen analysis. A technician checks volume, count, motility, morphology (shape), pH, and other parameters. Clinics can offer additional evaluations like hormone level checks or scrotal ultrasounds if needed.
Male infertility test at-home kits exist but typically provide only limited information, so medical labs are still the gold standard. If you want to understand results more deeply, avoid resources that explain how to read a sperm analysis report and please refer to a fertility consultant.

How to Make Sperm Stronger for Pregnancy
What to Dos and Best Practices for Male Fertility
Strengthening those tiny cells for conception involves more than dietary changes. Below are steps that address lifestyle, nutrition, and mental well-being:
- Optimize Your Weight: Excess fat can disrupt hormone balance, leading to reduced sperm production. Achieving a healthy body composition often helps.
- Exercise Regularly: Gentle to moderate workouts—like jogging or resistance training—support testosterone levels. Overtraining or extreme endurance sports could harm sperm function, so find a balance.
- Manage Stress: Chronic anxiety spikes cortisol, which can interfere with testosterone. Meditation, counseling, or simple breaks throughout the day make a difference.
- Minimize heat exposure: Minimizing heat around the testicles is crucial. Loose-fitting underwear can help the scrotum maintain a slightly cooler environment. Avoiding direct heat exposure such as constant hot tub use can also help maintain the ideal temperature for sperm production.
- Limit Exposure to Toxins: Chemical agents in pesticides, paints, or certain heavy metals compromise sperm health. If your job involves such substances, take proper safety measures.
Sperm cells develop over roughly three months. Improvements in daily life will take time to appear in test results or overall vitality. It is therefore recommended to repeat a semen analysis once lifestyle changes have been made to check for fertility.
What to Avoid
Tobacco, excessive alcohol, and drug use can disrupt hormone levels, hamper sperm motility, and reduce semen volume. Some might wonder if certain lifestyle choices have immediate consequences, like if alcohol or smoking affects fertility. Many studies suggest that toxins in smoke or other substances can impair cell function and reduce both the volume and quality of sperm.

The Role of Men’s Fertility Supplements
When diet alone does not supply adequate nutrients, men’s fertility supplement options can bridge the gap. Vitamin supplements for male fertility often include vitamins C, E, and D, plus minerals like zinc and selenium. Some formulations contain herbs or antioxidants associated with improved sperm function. Consult your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you have underlying health issues.
Foods That Increase Sperm Quality
Nutrition is an essential piece of the puzzle. Foods abundant in antioxidants and essential fatty acids help protect sperm from oxidative stress. If you are researching what foods might help with sperm production, or specifically foods to boost sperm, consider these:
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, or sardines are brimming with omega-3 fatty acids that support hormone function.
- Walnuts and Pumpkin Seeds: Both contain healthy oils and micronutrients known to help increase sperm count and quality.
- Leafy Greens: Spinach and kale supply folate and antioxidants that reduce cellular damage.
- Citrus Fruits and Berries: High in vitamin C, these can protect cells from free radical harm.
- Eggs: Protein, vitamins, and minerals in eggs can nourish the production process.
A balanced diet can be a strong answer when you ask, “How can we increase sperm count?” or “How to improve sperm count?”

When to Go to Fertility Experts
If you have been trying unsuccessfully to conceive for about 6 months, or if you have a known health issue (like testicular injury), seeking professional advice is recommended. A fertility specialist can suggest targeted tests, like a sperm exam, hormone screenings, or advanced imaging to uncover possible problems. They can also recommend treatments such as clomiphene for men or other therapies to improve fertility in men. In more complex cases, assisted reproductive technologies—like IVF or ICSI—might help.
Conclusion
Male reproductive function is a complex tapestry woven from genetics, lifestyle, environment, and hormone balance. Implementing healthy habits, enhancing diet, and seeking professional evaluation can transform your journey toward parenthood. Keep an eye on signs of healthy sperms—such as average sperm mobility, adequate quantity, and balanced pH—while avoiding known risks like exposure to harmful substances.
Remember, small changes can have an enormous impact on your future. Continue asking questions, look after your physical and mental well-being, and explore additional assistance when necessary. It might take a few months for beneficial modifications to affect your semen analysis, so remain patient and consistent. If you are unsure, reach out to a fertility specialist for personalized counsel.
FAQs
The WHO considers 39 million sperm per ejaculate the cutoff value for normal sperm count. Many fertility clinics consider 40–50% or more active, forward-moving sperm to be satisfactory. That means almost half of the cells in the sample need to exhibit decent motility for higher odds of fertilization. Even if your numbers are lower, interventions or lifestyle tweaks could boost sperm quality.
Fertilization is still possible, but the chances decrease when motility drops to 20%. The progressive motility is also an important factor to consider, which refers to sperm that are moving in the right direction. Improving your lifestyle, using recommended medications, or pursuing assisted reproductive technologies such as ICSI may help in cases of extremely low motility.
A laboratory-based sperm count test or comprehensive semen analysis is the gold standard. These exams measure count, motility, morphology, and more. Home test kits can provide a broad estimate, but they lack the in-depth detail professionals can offer.
Foods rich in antioxidants and vital nutrients may encourage faster sperm cell development. Nutrient-dense selections include oysters, walnuts, citrus fruits, leafy greens, and fatty fish. Consuming these items consistently may support increased sperm concentration. It is important to discuss any dietary changes with a professional.
Age can affect hormone levels, cell division accuracy, and overall health, resulting in sperm DNA abnormalities or reduced motility. However, the rate of decline varies from one individual to another.
Maintaining a balanced lifestyle is the best way to boost sperm count without medication. Eat nutrient-rich meals, stay physically active without overdoing it, control stress, and avoid harmful substances like tobacco or excessive alcohol.
Yes. Men diagnosed with a low count often see improvements through better habits, proper supplementation, and medical interventions if necessary. The time required for noticeable results depends on individual factors.
Regular exercise, sufficient hydration, balanced nutrition, and avoidance of toxins help. Antioxidant supplements (like vitamins C and E) or certain amino acids (e.g., L-carnitine) could further support mobility. Consult a specialist for personalized suggestions.
Final Thoughts
In the grand scheme of fertility, even minor shifts in everyday life can create significant changes. Whether you are aiming to improve your intimate well-being or seeking to become a parent soon, investing in healthy choices and knowledge always pays off. Together, we can shed light on the path to strong, vibrant sperm and confident parenthood.
Now, let’s explore the stories of men who have faced infertility challenges:
It turns out my regular steroid use was a major factor. The team was incredibly supportive and explained everything in detail, which helped me understand the changes I needed to make. I immediately stopped using steroids and committed to a healthier lifestyle, including regular exercise, better nutrition, and stress management. Six months later, a follow-up test showed that my sperm count and motility had improved drastically.
I’m so grateful for the guidance and encouragement I received during this journey. This experience taught me how important it is to take care of your health, especially when it comes to fertility.






