Facing a cancer diagnosis is life-altering, and for men of reproductive age, concerns about future fertility add another layer of complexity. Cancer treatments like chemotherapy, radiation, and certain surgeries can significantly impact male fertility. Understanding these risks and exploring preservation options is crucial for those wishing to maintain the possibility of biological parenthood.

The Impact of Cancer Treatments on Male Fertility
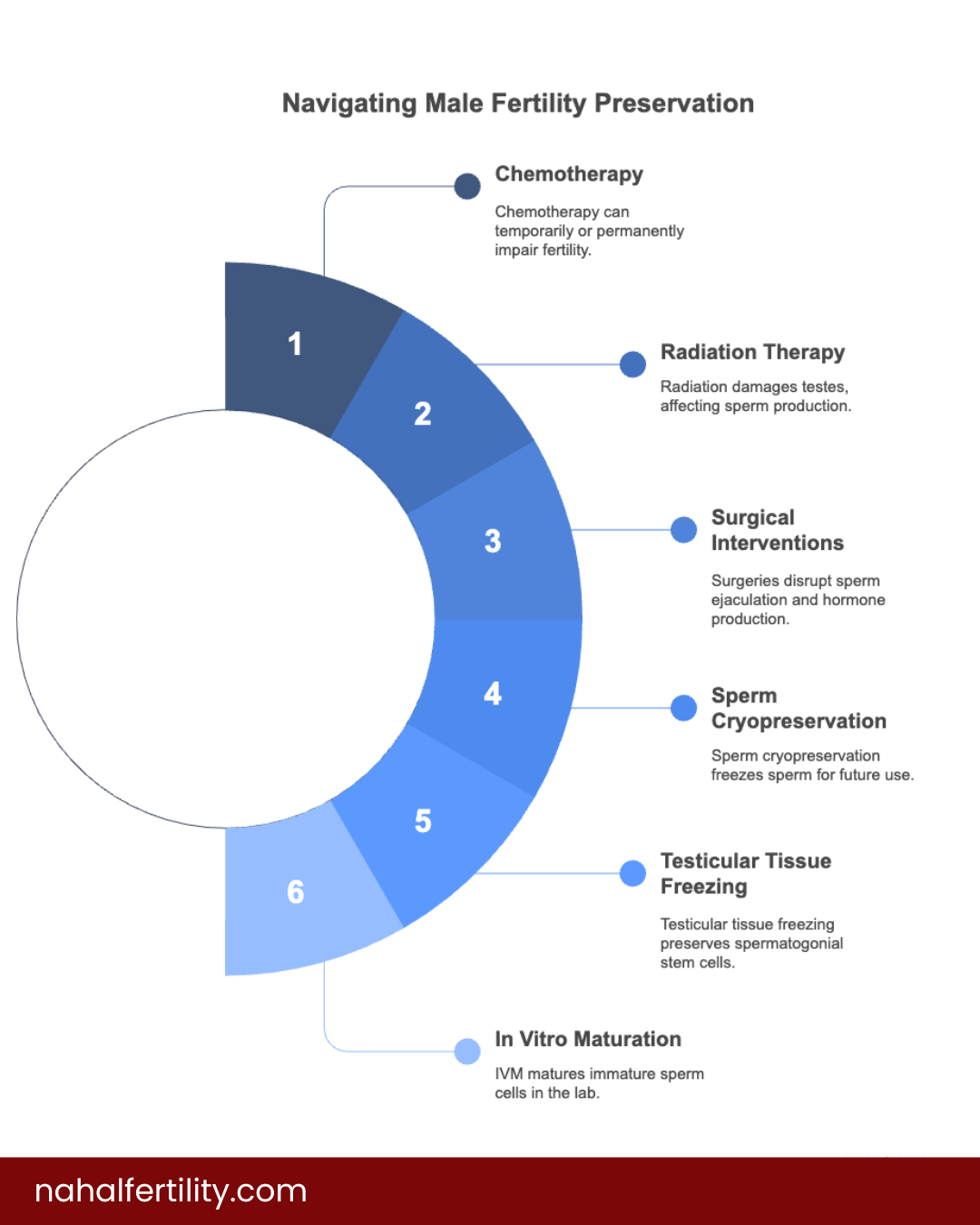
Chemotherapy and Fertility
Chemotherapy targets rapidly dividing cells, which unfortunately includes sperm-producing cells. The extent of fertility impairment depends on factors like the type and dose of chemotherapy, as well as the patient’s age. Some men may experience temporary infertility, while others may face permanent effects. Recovery of sperm production can take months or even years, and in some cases, it may not return to pre-treatment levels.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation directed near the pelvic area can damage the testes, affecting sperm production. The risk increases with higher doses and larger treatment areas. Shielding techniques can sometimes protect the testes during radiation, but they may not eliminate the risk entirely.
Surgical Interventions
Surgeries involving the reproductive organs, such as orchiectomy (removal of one or both testicles) or procedures affecting the prostate and seminal vesicles, can directly impact fertility. These surgeries may disrupt the pathways necessary for sperm ejaculation or hormone production.
Fertility Preservation Options
Sperm Cryopreservation
Also known as sperm banking, this is the most established method for preserving male fertility. It involves collecting and freezing sperm samples for future use. Ideally, samples should be collected before starting cancer treatment.
Testicular Tissue Freezing
For prepubescent boys who cannot produce mature sperm, experimental techniques like testicular tissue freezing are being explored. This involves preserving testicular tissue that contains spermatogonial stem cells, with the hope of maturing them into sperm in the future.
In Vitro Maturation (IVM)
IVM is an emerging technique where immature sperm cells are matured in the laboratory. While primarily used in female fertility preservation, research is ongoing to adapt this method for male patients.
The Importance of Early Intervention
Discussing fertility preservation with healthcare providers before starting cancer treatment is essential. Early intervention allows for a broader range of preservation options and increases the likelihood of future biological parenthood. Oncologists and fertility specialists should work collaboratively to inform patients about the risks and available strategies.
Conclusion
Cancer treatments can significantly impact male fertility, but proactive measures can help preserve reproductive potential. By understanding the risks and exploring preservation options like sperm banking, testicular tissue freezing, and emerging technologies, men can make informed decisions about their reproductive futures. Early consultation with healthcare providers is key to navigating these choices effectively.






