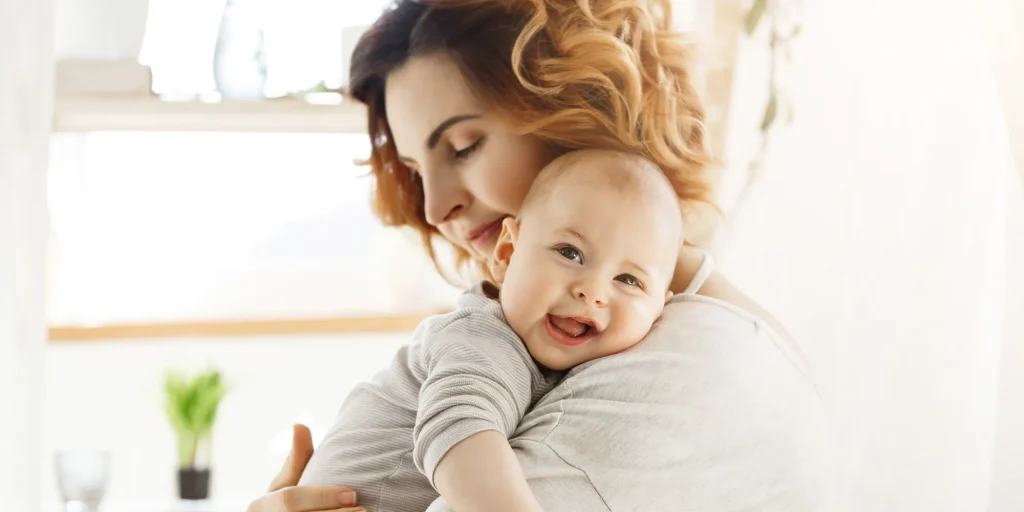
What is Frozen Blastocyst Transfer?
Frozen blastocyst transfer (FBT) is an advanced in vitro fertilization (IVF) technique where a previously frozen embryo is thawed and transferred into the uterus. This method allows patients to optimize their chances of pregnancy by transferring only high-quality embryos at the most optimal time in the menstrual cycle.
At Nahal Fertility, we specialize in frozen embryo transfer (FET) treatments, offering personalized care and state-of-the-art reproductive technology to help individuals and couples achieve their dream of parenthood.
Step-by-Step Process of Frozen Blastocyst Transfer
How Frozen blastocysts (Embryo Transfer) Works?
Preparing the Uterus
A personalized hormonal regimen prepares the uterus for implantation. Estrogen and progesterone help thicken the uterine lining. Blood tests and ultrasounds monitor progress, ensuring the best conditions before transfer.

Embryo Thawing
The selected frozen embryo is carefully thawed by embryologists. Advanced techniques ensure the embryo remains viable and ready for implantation. Once warmed, it is examined for quality before the transfer.

Embryo Transfer
A thin catheter is used to place the embryo into the uterus under ultrasound guidance. This quick, painless procedure takes minutes, requiring no anesthesia. Patients can resume light activities the same day.

The Two-Week Wait
During this phase, implantation may occur. Mild cramping, spotting, or bloating are common signs. Patients should continue prescribed medications. A beta hCG blood test is taken 10-14 days after transfer to confirm pregnancy.
Optimizing Your Chances of Frozen Blastocyst Transfer Success
To enhance the likelihood of implantation and pregnancy, patients should:
Follow all post-embryo transfer care instructions from their fertility specialist.
Maintain a healthy diet, stay hydrated, and rest adequately.
Avoid excessive physical strain and stress.
Monitor symptoms carefully but avoid overanalyzing every sign.
Why Choose Frozen Blastocyst Transfer?
Frozen embryo transfer has revolutionized fertility treatments, providing significant advantages over fresh transfers. Here’s why more patients are choosing FBT:
Higher Success Rates: Studies show that frozen embryo transfer success rates are comparable to or even higher than fresh transfers, as the uterus is in a more natural and receptive state.
Better Endometrial Preparation: With frozen embryo transfer, the uterine lining has more time to thicken and become optimal for implantation.
Genetic Testing Compatibility: Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) can be performed on embryos before freezing, ensuring only healthy embryos are transferred.
Flexible Timing: Unlike fresh transfers, which must be done immediately after egg retrieval, frozen blastocyst transfer allows patients to prepare their bodies for implantation at the best time.
Start Your Journey to Parenthood with Nahal Fertility
Ready to take the next step? Schedule your consultation today!
FAQs
Typically, implantation occurs 1-5 days after embryo transfer as the blastocyst attaches to the uterine lining.
Frozen Blastocyst Transfer (FBT) is a type of Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET) where only blastocyst-stage embryos (typically 5 or 6 days old) are transferred. In contrast, FET can involve embryos at any stage of development, including cleavage-stage embryos (3 days old). FBT is often preferred due to its higher implantation success rates.
A beta hCG test is recommended 10-14 days after embryo transfer for accurate results.
Early pregnancy symptoms like mild cramping, implantation spotting, and fatigue may be positive indicators.
Light activities like walking are safe, but high-impact exercise should be avoided.
Frozen embryo transfer (FET) is typically performed between days 19 and 21 of a woman's menstrual cycle in a hormonally controlled cycle. In a natural cycle, the transfer is scheduled based on ovulation, usually 5 to 7 days after ovulation. The exact timing depends on uterine lining development and hormone levels, ensuring the best chance for implantation.
Embryo transfer in IVF typically occurs 3 to 5 days after egg retrieval when using fresh embryos. If opting for frozen embryo transfer (FET), the procedure is scheduled based on the patient's cycle, usually 5 to 7 days after ovulation in a natural cycle or on cycle days 19-21 in a hormonally controlled cycle. The timing ensures the uterine lining is receptive for implantation.
